 |
 |
- Search
| Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg > Volume 26(3); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Various methods for reconstructing partial upper lip defects have been reported, some of which, such as the Abbe and Estlander flaps, involve using the lower lip. However, determining the appropriate reconstruction method for large upper lip and oral commissure defects is particularly difficult because of the need to preserve the function and sensory ability of the lips and oral sphincter while achieving a satisfactory appearance. We describe our successful experience of using an extended Estlander flap to reconstruct a large defect caused by the excision of basal cell carcinoma on the upper lip and oral commissure.
The Estlander flap is most commonly used to repair full-thickness defects of the lip involving the oral commissure. In this method, a well-perfused axial flap supplied by the superior or inferior labial artery is applied. If the defect is not severe, it is important to simultaneously reconstruct the labial unit or subunit for aesthetic purposes [1]. Traditionally, the flap extends to the mental crease. However, in cases of large upper lip defects, reconstruction using only the traditional Estlander flap is insufficient since a wider donor site beyond the mental crease is required. Thus, defects extending beyond the confines of the upper lip can be reconstructed using an extended Estlander flap, which is supplied by the inferior labial artery. Injection studies of the inferior labial artery in cadavers by Kriet et al. demonstrated that the cutaneous territory of this artery comprises the entire lower lip and chin and a significant portion of the submental skin [2-4]. The application technique for the extended Abbe flap in these injection studies was referred to when designing the extended Estlander flap for this case. This article describes the authors’ experience of using the extended Estlander flap for reconstructing a large upper lip defect involving the oral commissure.
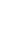
A 51-year-old man visited our department for basal cell carcinoma affecting the upper lip, columella, nasal sill, ala nasi, and nasolabial area. On physical examination, the mass was an irregularly shaped ulcerative lesion measuring 3.0×3.5 cm (Fig. 1A). No distant metastases were identified on neck computed tomography or facial magnetic resonance imaging.
Under general anesthesia, the mass was excised with a safety margin of 5 mm (Fig. 1B). After excision of the tumor, an extended Estlander flap was applied, along with right perialar crescentic excision and a left cheek advancement flap (Fig. 1C). To advance sufficient tissue, the flap of the left cheek was designed to be larger than the other flaps. We performed an advancement flap to address the columellar defect (Fig. 1D). Six months later, the patient exhibited asymmetric lips and incomplete mouth opening (Fig. 2). Therefore, Kazanjian-Roopenian type I commissuroplasty was performed to correct the lip asymmetry by lengthening the left oral commissure (Fig. 3A). Postoperative complications, such as venous return disturbance, infection, and seroma were not observed. Oral ingestion was possible immediately after surgery. Although minimal bilateral asymmetry persisted, the mouth could be opened sufficiently, and the oral commissure was symmetrical after commissuroplasty. The Semmes-Weinstein monofilament test, intramuscular electromyography, and nerve conduction velocity testing were performed 36 months after surgery, and the results indicated normal recovery of the sensory and contractile functions of the lips (Tables 1,-3). The stimulator was attached to the skin of the base of the facial nerve. The recorder was attached to the skin of the corresponding muscle. The time to reach the recorder was measured after stimulation was given. The right zygomatic branch of the facial nerve was tested from the right ear to the right orbicularis oculi. The right buccal branch of the facial nerve was tested from the right ear to the right orbicularis oris. The left zygomatic branch of the facial nerve was tested from the left ear to the left orbicularis oculi. The left buccal branch of the facial nerve was tested from the left ear to the left orbicularis oris (Tables 1, 2). At a 39-month follow-up, we observed improvement in the functional and aesthetic aspects of the lips (Fig. 3B).
Lips are involved in several complex functions, including emotional expression, oral sphincter function, and speech articulation. Lips are also a symbol of aesthetic beauty. The primary aim of lip and oral commissure reconstruction is the preservation of function. Oral competence, muscle function, lip sensation, and adequate mouth opening are the four main goals for achieving normal oral function. The cosmetic aims of lip reconstruction include restoring labial symmetry at rest and when animated. However, oral competence and lip function, rather than cosmetic factors, are the key determinants of successful lip reconstruction [5-8].
An appropriate lip reconstruction method should be chosen according to the defect size. Reconstruction of large upper lip defects is a major challenge for plastic surgeons. The traditional Estlander flap is a popular method for reconstructing small upper lip defects involving the oral commissure, but is insufficient for repairing larger defects. In 1995, Kriet et al. [4] successfully reconstructed a large defect of the upper lip using an extended Abbe flap. Thereafter, this procedure has been often used by plastic surgeons because of excellent aesthetic and functional outcomes after reconstruction. We referred to the extended Abbe flap application technique and applied it to design an extended Estlander flap. Normally, the cutaneous territory of the inferior labial artery is within the mental crease; therefore, the flap should not exceed the mental crease. The extended Estlander flap is especially suitable for treating large defects of the upper lip, including resection of the oral commissure and alar base. This case demonstrated good results both in terms of aesthetic and functional aspects. Although we performed this procedure in only one patient, we believe that the extended Est lander flap is a good reconstructive option for patients with large defects of the upper lip.
Notes
Ethical approval
The study was performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Patient consent
The patient provided written informed consent for the publication and the use of his images.
Fig. 1.
(A) Preoperative excision outline. (B) After excision. (C) Intraoperative design of the extended Estlander flap and left cheek advancement flap. (D) Immediate postoperative image.
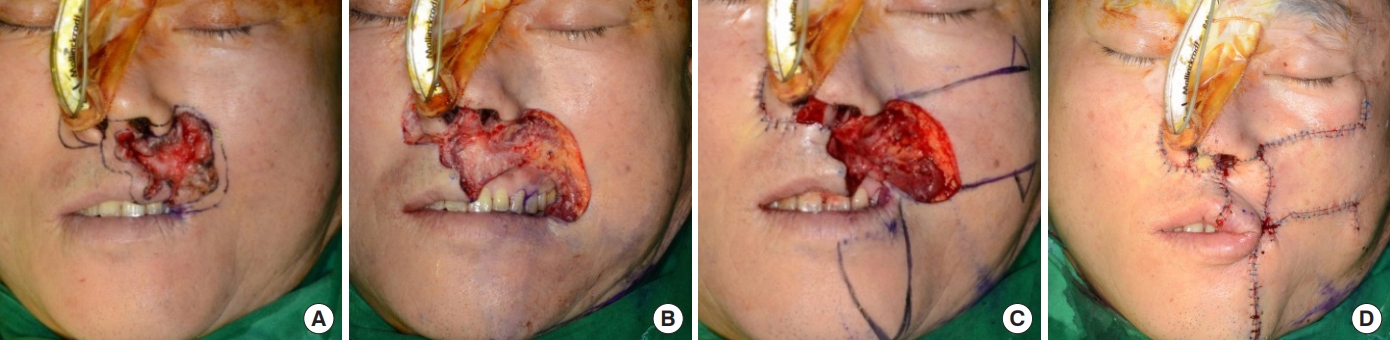
Fig. 2.
Postoperative outcome at 6 months after extended Estlander flap application. Asymmetry of the oral commissure and microstomia are observed. (A) Close mouth view. (B) Open mouth view.

Fig. 3.
Postoperative outcome at 3 years after extended Estlander flap application. Microstomia was improved and asymmetry of the oral commissure was corrected than before. (A) Kazanjian-Roopenian type I commissuroplasty. (B) Open mouth view.

Table 1.
Nerve conduction velocity test results
Table 2.
Needle electromyography interpretation
The electrode attached to the muscle was connected to electromyography to observe the waveform. Positive shock waves (PSWs) and fibrillation were observed with the muscle in its resting state. Recruitment, amplitude, duration, and polyphasic waveforms were observed after slight contracture of the muscle. The same results were obtained on the affected side and the uninjured side.
REFERENCES
1. Kim NG, Lee KS. Lower lip reconstruction using various flap surgeries. J Korean Cleft Palate-Craniofac Assoc 2004;5:94-100.
2. Naficy S, Baker SR. The extended Abbe flap in the reconstruction of complex midfacial defects. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2000;2:141-4.


3. Whetzel TP, Mathes SJ. Arterial anatomy of the face: an analysis of vascular territories and perforating cutaneous vessels. Plast Reconstr Surg 1992;89:591-603.


4. Kriet JD, Cupp CL, Sherris DA, et al. The extended Abbé flap. Laryngoscope 1995;105(9 Pt 1): 988-92.


5. Yamauchi M, Yotsuyanagi T, Ezoe K, et al. Estlander flap combined with an extended upper lip flap technique for large defects of lower lip with oral commissure. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2009;62:997-1003.


6. Alvarez GS, Siqueira EJ, de Oliveira MP. A new technique for reconstruction of lower-lip and labial commissure defects: a proposal for the association of Abbe-Estlander and vermilion myomucosal flap techniques. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2013;115:724-30.









