 |
 |
- Search
| Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg > Volume 26(4); 2020 > Article |
|
See commentary "Comments on ŌĆ£Reduction malarplasty combined with facelift via the prezygomatic spaceŌĆØ" in Volume 27 on page 80.
See commentary "Re: Comments on ŌĆ£Reduction malarplasty combined with facelift via the prezygomatic spaceŌĆØ" in Volume 27 on page 116.
See commentary "Re: Comments on ŌĆ£Reduction malarplasty combined with facelift via the prezygomatic spaceŌĆØ" in Volume 27 on page 116.
Abstract
Background
In Asian women who undergo facelift surgery, satisfactory results are typically achieved with regard to facial rhytides, but concerns have been reported regarding the postoperative appearance of the malar prominence region. Anatomically, compared to Caucasians, Asians have thick skin and a wide and short facial geometry. Asians generally exhibit zygomatic protrusion; accordingly, bone contouring surgery, which alters the base frame used in a facelift, should be considered. We aimed to investigate the effects of simultaneous reduction malarplasty and facelift to achieve appropriate malar repositioning and a youthful-looking face.
Methods
We assessed 16 Asian women who underwent simultaneous reduction malarplasty and facelift between March 2014 and March 2018. The clinical results were assessed based on preoperative and postoperative photographs and Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale scores.
Results
Surgery was successful in all cases. Postoperative improvement with regard to facial rhytides and appropriate malar repositioning were achieved. All patients were satisfied with the outcomes. Some patients experienced short-term complications, but their conditions improved. Serious long-term complications were not noted.
The demand for facial rejuvenation surgery is increasing with the increase in the elderly population. Among surgical treatments, facelift is widely used to lift the soft tissue, weaken the nasolabial groove, and provide volumetric fullness to the face [1]. However, due to differences in the anatomical structures of the faces of Asians and Caucasians, this method currently does not yield satisfactory outcomes for all Asian women. The faces of Asians differ from those of Caucasians with respect to the skull structure and facial fat. Relative to Caucasians, Asians generally have a wider and flatter face, a greater bizygomatic distance, and a less developed premaxilla. Moreover, the facial fat is fully distributed in the malar and submalar regions in Asians. As Asian individual ages, the facial fat descends, and the face becomes more rectangular and boxy [2,3]. For these reasons, some older Asian women exhibit zygomatic protrusion and wide faces. In these patients, performing only a soft tissue facelift will cause the face to look wider and the zygoma to appear more protruded.
In Asian culture, an overly protruded zygoma and wide face are undesirable because they suggest an unaesthetic and harsh appearance. When facelift is performed in isolation, without consideration of this cultural feature, patients with zygomatic protrusion often complain that their face looks wider after surgery.
Therefore, it can be concluded that without considering the cultural and anatomical differences between Asians and Caucasians, the soft tissue alone does not provide satisfactory results for Asian women with zygomatic protrusion.
To resolve such issues, we aimed to perform reduction malarplasty to reposition the malar highlight ideally during facelift. We report this surgical technique and discuss its effects.
This study included 16 Asian women who underwent simultaneous reduction malarplasty and facelift between March 2014 and March 2018. The mean age of the patients was 52 years; smokers and patients with concomitant medical illnesses were excluded.
The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Eulji University Hospital (approval No. EMC 2019-12-005-001). Informed consent was provided by all subjects prior to enrollment.
All surgical procedures were performed under general anesthesia through orotracheal intubation. To minimize intraoperative bleeding, surgery was performed approximately 15 minutes after the administration of tumescent solution. An incision that followed the temporal hairline, tragal margin, and occipital hairline was made, after which the skin flap was elevated. To release the subcutaneous points of attachment of crowŌĆÖs feet and to achieve smooth redraping of the temporal skin, subcutaneous dissection was performed above the zygomatic arch of the lateral orbital area. A vertical incision was made along the superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) 1 cm anterior to the preauricular skin incision; this was followed by SMAS dissection. By dissecting anteriorly and inferiorly along the SMAS, the orbicularis oculi and platysma were connected and included in the SMAS flap. The main zygomatic and upper masseteric retaining ligaments were carefully released to avoid facial nerve injury.
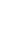
After sufficient elevation of the SMAS flap, the prezygomatic space between the orbicularis oculi and the zygomaticus muscles was approached. The orbicularis retaining ligaments and the zygomaticofacial nerve could be seen with the naked eye. A vertical incision of about 2 cm was made from the right side of the orbicularis retaining ligaments and the zygomaticofacial nerve to the origin of the zygomaticus muscles on the preperiosteal fat (Fig. 1). After careful elevation of the subperiosteal flap along the vertical incision, the zygomatic body was exposed, and a reciprocating saw was used to perform the osteotomy.
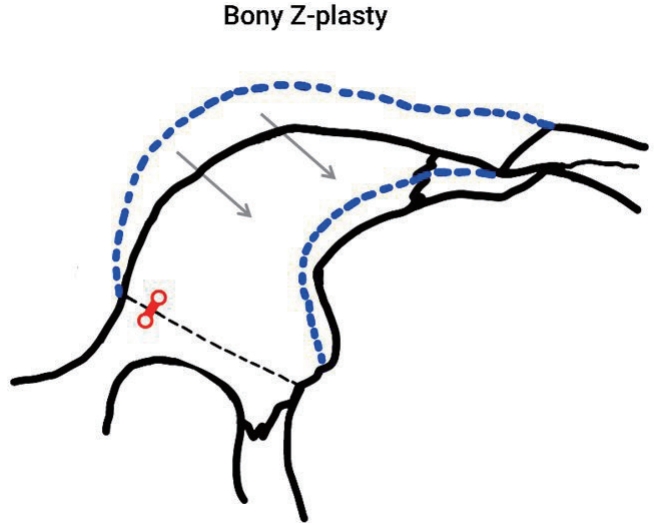
Subsequently, a preauricular incision of approximately 1.5 cm was made for a bony Z-plasty, and the zygomatic process of the temporal bone was exposed through the periosteal dissection. The reciprocating saw was used for the osteotomy and bony Z-plasty (Figs. 2, 3). When warranted, a two-hole miniplate was used to achieve fixation of the zygomatic body after the bony Z-plasty (Fig. 4).
After the completion of the reduction malarplasty, the SMAS flap was redraped on the cheek. The SMAS flap was pulled parallel to the long axis of the zygomaticus major and to the edge of the original SMAS incision. The redundant tissue was then removed. The preauricular SMAS flap was postauricularly transposed and fixed to the mastoid fascia. The cheek skin flap was horizontally redraped, and the redundant skin was removed. The skin was closed with minimal to no tension. A negative suction drainage catheter was used, and a gentle compression dressing was applied.
The postoperative results were assessed using preoperative and 6-month postoperative photographs and Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS) scores by a blinded investigator (Table 1).
A total of 16 patients underwent reduction malarplasty with facelift in this study. The median operative time was 238 minutes (range, 215ŌĆō272 minutes). The patients were discharged 1 day postoperatively and were examined on the third day postoperatively. The sutures were removed on postoperative day 7. A compression dressing with an elastic bandage was used for 7 days, after which an elastic mask was worn. A soft diet was recommended for at least 3 days postoperatively. Routine follow-up was performed at 3 and 6 months postoperatively.
All patients were satisfied with the results, and no serious complications were noted. No side effects such as unexpected bone fracture or facial nerve injury were reported. Two patients experienced unilateral numbness of the skin in the malar area, but this symptom abated by 6 months postoperatively. One patient experienced scar widening. After proper scar revision, satisfying results were obtained. The surgical results were assessed using GAIS scores. Two (12.5%) patients had GAIS scores of 1; six (37.5%) patients had scores of 2, and eight (50.0%) patients had scores of 3 (Table 2, Figs. 5-7).
For patients undergoing facelift procedures, the aim is not only to remove wrinkles via simple skin tightening, but also to achieve a three-dimensionally young-looking face. Accordingly, both the sagging of the soft tissue as a consequence of aging in the midfacial area and its association with the descent of the malar bone should be considered. As one ages, due to changes to the facial bone, the facial width increases, and bony prominences become coarsened [4,5]. Satisfactory results cannot be obtained if facelift is performed in isolation without considering the changes of the facial bone structure that occur with aging.
Anatomically, compared with Caucasians, Asians have thick skin and a wide and short facial geometry [6,7]. Asians also have a distinct facial contour, characterized by a brachycephalic cranium with a protruded zygoma. These features result in a wide facial contour, which is considered unaesthetic and masculine in Asian culture. Culturally, Asian facial beauty is characterized by a small face. Patients with zygomatic protrusion often report their faces looking wider after surgery when facelift was performed in isolation without considering this cultural difference. For patients with such features, it is difficult to obtain satisfying results with simple facial rejuvenation. The presence of a more protruded zygoma following improvement with regard to rhytides is one concern that has been reported after facelift by some Asian women with wide faces. Therefore, it can be concluded that in such cases, lifting the soft tissue alone, without considering the cultural and anatomical differences between Asians and Caucasians, does not provide satisfactory results.
Although methods for facial rejuvenation such as implant insertion and volumetric restoration using fat grafting are available [8,9], these methods are associated with complications such as infection, implant displacement, bony absorption, and contour irregularity. In contrast, the facelift technique involves the suspension of the subcutaneous fat mass of the mandibular and malar regions in the cheek area; via this technique, facial rhytides can be effectively improved, and long-lasting results can be achieved [10]. It is clear that facelift can reduce the depth of the nasolabial fold and improve both the jowl and the jawline to yield a more youthful appearance. In order to achieve more effective aesthetic results. Skeletal support is important for soft tissue repositioning; therefore, the facial skeleton should be considered before such repositioning is performed [11]. This is critical because the primary goal of facelift is the improvement of the facial appearance, not just the treatment of rhytides. Particularly in Asian women with zygomatic protrusion, it is difficult to obtain an attractive facial contour without considering the supporting bone. We attempted to reposition the malar highlight of the bony support in individuals with wide faces to achieve a more attractive facial appearance.
Reduction malarplasty is one of the most frequently performed facial bone contouring procedures in Asians. In the past, this procedure included only simple reduction because the main goal was to make the face look smaller. However, this procedure can have side effects such as soft-tissue descent resulting from subperiosteal dissection, and as a result, the malar highlight may not be repositioned optimally. Reduction alone cannot have a significant effect in elderly patients, and an opposite effect, caused by soft-tissue descent, may occur. Therefore, repositioning the malar eminence optimally and then performing a facelift procedure may yield better aesthetic results. In addition, as the zygoma is medially repositioned, the SMAS flap is more easily tightened, and the rhytidectomy may be more effective.
In general, reduction malarplasty is performed via an intraoral approach. However, when we performed surgery using the facelift technique, the prezygomatic space was accessible, allowing us to adequately perform reduction malarplasty. Mendelson et al. [12] first presented the concept of the prezygomatic space. In the sub-SMAS plane, the boundaries of the space are established by the facial retaining ligaments. The prezygomatic space is located below the orbicularis oculi and above the zygomatic prominence. The orbicularis retaining ligament (superiorly) and the zygomatic ligament (inferomedially) form a triangular space. Because no structures are housed in or pass through this area of the prezygomatic space, safe dissection is possible, and the risks of bleeding and facial nerve injury are minimized. Using the prezygomatic space, the zygomatic eminence can be approached safely via subperiosteal dissection. After subperiosteal dissection, a resection line for the osteotomy is made on the zygomatic body, and the bone is cut safely using a reciprocating saw.
The main disadvantage of the use of this method in Asian patients is the possibility of hematoma caused by bleeding, which occurs as a result of osteotomy. Therefore, it is necessary to proceed cautiously when performing a facelift to ensure that bleeding can be controlled. Other possible disadvantages include the long operative time, prolonged postoperative swelling of the surgical site, and steep learning curve. Facial nerve injury may be considered the most serious disadvantage of this technique; however, this complication has not yet been reported. When using this surgical method, damage to the facial nerve should be avoided by limiting the incision to the prezygomatic space that exists between the orbicularis retaining ligament and the zygomatic retaining ligament.
Compared to traditional malar reduction requiring an intraoral approach, our approach has a shorter recovery time and a lower possibility of infection. In addition, as the SMAS flap acts as a compression garment, side effects such as malunion, nonunion, and stepping deformity are rare. To summarize, our surgical method enables faster recovery by reducing the excess trauma associated with surgery in Asian women who want to undergo reduction malarplasty simultaneously with facelift. Our method also has reduced postoperative complications, such as infection and delayed surgical recovery, while producing satisfying results for the patient. Zou et al. [13] used an intraoral approach to perform reduction malarplasty combined with facelift. The advantages of that method are that it is relatively easy for the operator to learn and the operative time is short. However, compared with our technique, their method may have a longer recovery time and a higher possibility of infection resulting from their use of an intraoral approach.
In a similar study, Baek and Lee [14] performed reduction malarplasty and facelift with a bicoronal approach. Via a subperiosteal dissection, that method can be used to perform a simultaneous forehead lift and has the advantage of a clear field of view. However, it excessively burdens patients because of the broad surgical site and has risks including a long scalp scar, alopecia, and temporal depression.
Compared with those two methods, we can confirm that our method is associated with less trauma from surgery, allows patients to recover more quickly, and has fewer postoperative side effects, such as the possibility of infection and alopecia. Furthermore, if a surgeon overcomes the steep learning curve and becomes familiar with the anatomy of the prezygomatic space and this surgical method, we believe that zygomatic repositioning can be performed more effectively and easily and with a more intuitive field of view than other surgical methods, via the safe use of a direct incision on the zygomatic body without facial nerve injury.
In conclusion, reduction malarplasty combined with facelift appears effective and safe for Asian women with a protruded zygoma. By performing facelift combined with facial contouring surgery, we achieved high postoperative patient satisfaction and addressed the complications that may arise when facelift alone is performed for Asian patients with zygomatic protrusion. This surgical method may aid Asian women in safely and effectively regaining a youthful appearance.
Notes
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Eulji University Hospital (IRB No. EMC 2019-12-005-001) and performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Patient consent
The patients provided written informed consent for the publication and the use of their images.
Fig.┬Ā1.
Anatomy of the prezygomatic space. Anatomically, the space is located below the orbicularis oculi and above the zygomatic prominence. The orbicularis retaining ligament (superiorly) and the zygomatic retaining ligament (inferomedially) form a triangular space in the sub-superficial musculoaponeurotic system plane. Here, the zygomatic branches of the facial nerve extending to the orbicularis oculi do not penetrate this space. A vertical incision (shown in red) is made on the preperiosteal fat for subperiosteal flap dissection. LOT, lateral orbital thickening; OO, orbicularis oculi; ORL, orbicularis retaining ligament; SOOF, sub-orbicularis oculi fat; TFN, temporal branches of the facial nerve; ZFN, zygomaticofacial nerve; Zmaj., zygomaticus major; Zmin., zygomaticus minor; ZRL, zygomatic retaining ligament.
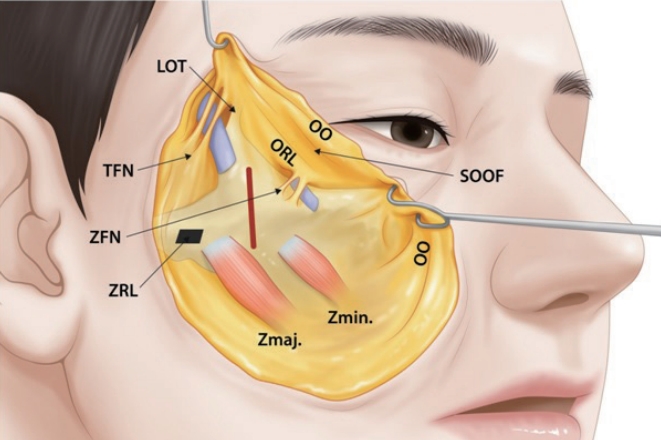
Fig.┬Ā2.
Facial bone contouring. (A) Osteotomy of the zygomatic body. (B) Osteotomy of the zygomatic arch for bony Z-plasty.
Fig.┬Ā4.
Preoperative (A) and postoperative (B) three-dimensional computed tomography. Two-hole miniplates were used to fix the zygomatic body.

Fig.┬Ā5.
A 40-year-old woman with a wide face and deepening of the nasolabial fold underwent reduction malarplasty with facelift. (A, C) Preoperative photograph. (B, D) Postoperative photograph taken 6 months later, in which the facial rhytides and malar contour appear greatly improved. Lifting of the malar fat pad and repositioning of the malar highlight can be observed. The patient was very satisfied with the results.
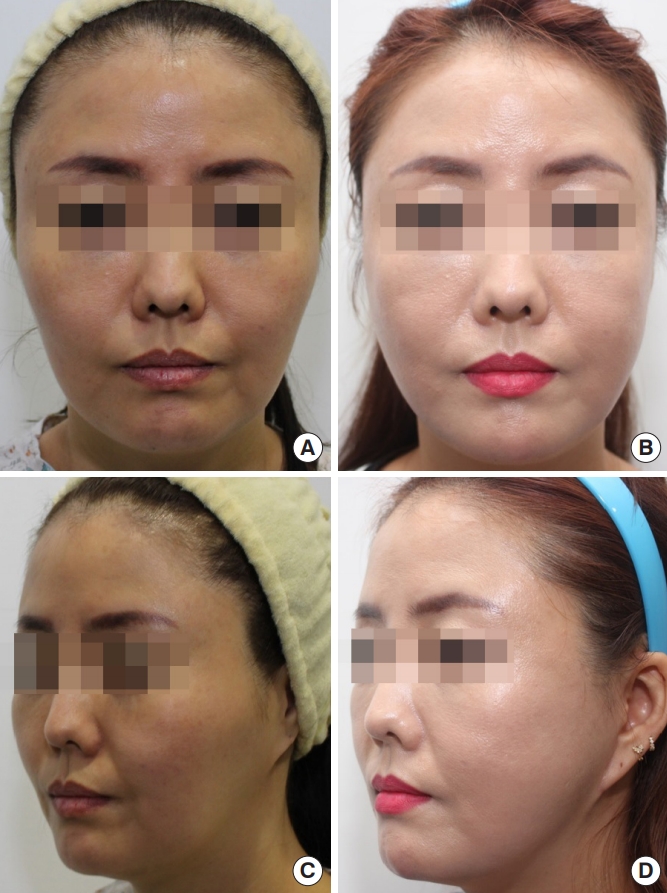
Fig.┬Ā6.
A 40-year-old woman with zygomatic protrusion and soft tissue sagging underwent reduction malarplasty with facelift. (A, C) Preoperative photograph. (B, D) Postoperative photograph taken 6 months later, in which the facial rhytides and malar contour appear greatly improved. Weakening of the nasolabial fold and repositioning of the wide and prominent mala can be seen in the postoperative photograph.
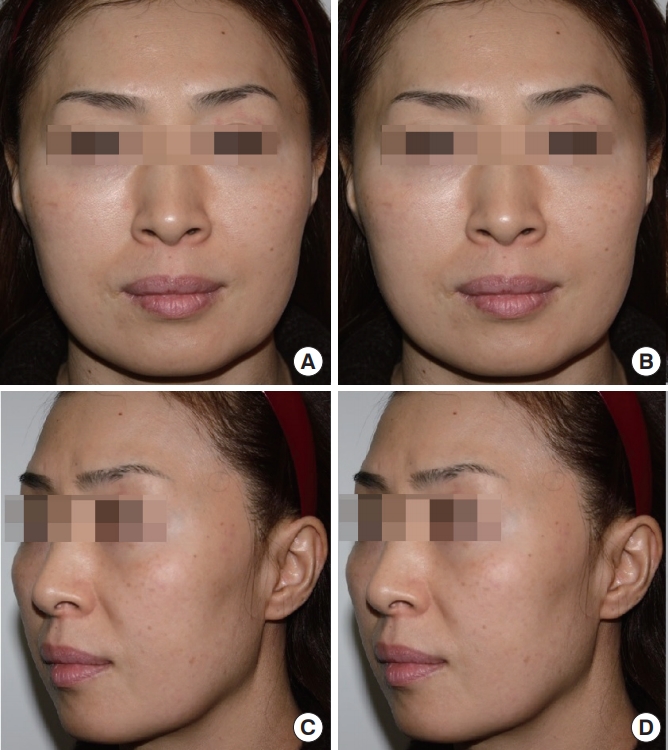
Fig.┬Ā7.
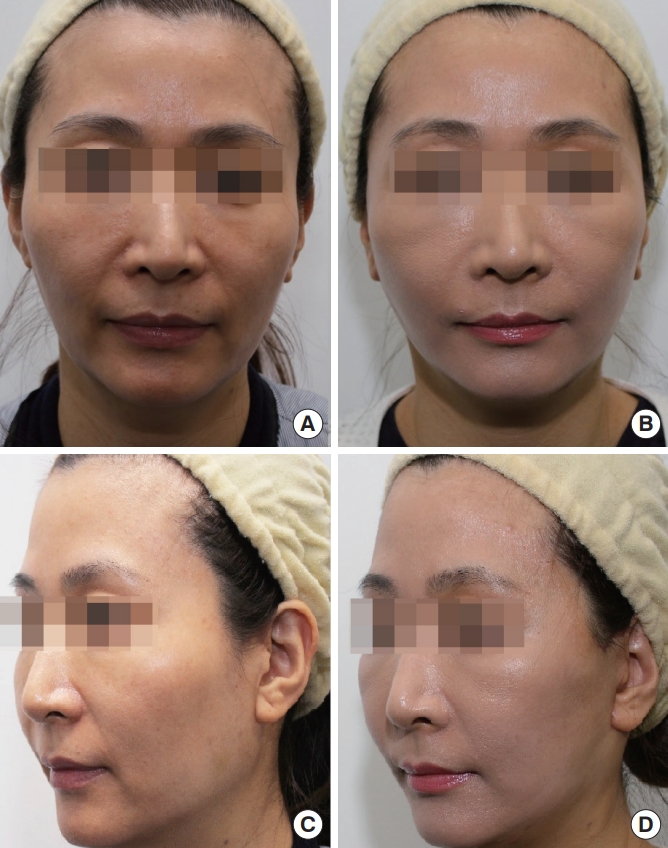
A 45-year-old woman with a wide face who appeared tired due to the sagging of soft tissue underwent reduction malarplasty with facelift. (A, C) Preoperative photograph. (B, D) Postoperative photograph taken 6 months later, in which the facial rhytides and malar contour appear greatly improved. Weakening of the nasolabial fold and superomedial repositioning of the malar highlight can be observed.
Table┬Ā1.
Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale scores
Table┬Ā2.
Assessment of surgical outcomes by Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale scores
REFERENCES
1. Collawn SS, Vasconez LO, Gamboa M, et al. Subcutaneous approach for elevation of the malar fat pad through a prehairline incision. Plast Reconstr Surg 1996;97:836-41.


2. Pessa JE. An algorithm of facial aging: verification of LambrosŌĆÖs theory by three-dimensional stereolithography, with reference to the pathogenesis of midfacial aging, scleral show, and the lateral suborbital trough deformity. Plast Reconstr Surg 2000;106:479-88.


3. Owsley JQ, Roberts CL. Some anatomical observations on midface aging and long-term results of surgical treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 2008;121:258-68.


4. Bartlett SP, Grossman R, Whitaker LA. Age-related changes of the craniofacial skeleton: an anthropometric and histologic analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 1992;90:592-600.


5. Shaw RB Jr, Kahn DM. Aging of the midface bony elements: a three-dimensional computed tomographic study. Plast Reconstr Surg 2007;119:675-81.


6. Onizuka T, Hosaka Y, Miyata M, et al. Our mini-facelift for Orientals. Aesthetic Plast Surg 1995;19:49-58.


7. Gu Y, McNamara JA Jr, Sigler LM, et al. Comparison of craniofacial characteristics of typical Chinese and Caucasian young adults. Eur J Orthod 2011;33:205-11.


9. Burres S. Midface volume replacement with a transmaxillary implant. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2005;29:1-4.


10. Barton FE Jr, Hunt J. The high-superficial musculoaponeurotic system technique in facial rejuvenation: an update. Plast Reconstr Surg 2003;112:1910-7.


11. Stuzin JM. Restoring facial shape in face lifting: the role of skeletal support in facial analysis and midface soft-tissue repositioning. Plast Reconstr Surg 2007;119:362-76.


12. Mendelson BC, Muzaffar AR, Adams WP Jr. Surgical anatomy of the midcheek and malar mounds. Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110:885-96.


-
METRICS

- Related articles in AAPS
-
Mandibular angle reduction combined with facelift via the premasseter space2020 October;26(4)